Anycast at a Glance
Availability on the Internet is a matter of course, both in business and private life. Be it websites, e-mail communication, webshops, online banking or media downloads – we expect them to be readily available and properly functioning at any time. All these services are accessed with the support of the Domain Name System (DNS), which resolves the domain names into IP addresses and thus enables us to call on them simply via the domain name.
The DNS is a core piece of the Internet and must therefore be robust, fail-proof, absolutely reliable and secure. A perfect solution to safely meet these requirements is the Anycast Name Service.
Unicast – Linear and Straightforward
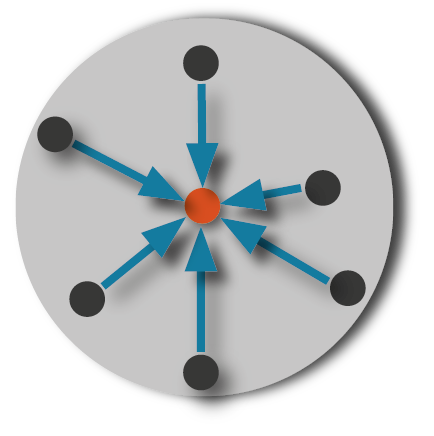
The traditional addressing method on the Internet is Unicast. With this method, a sender request is addressed to a dedicated receiver (destination). This means, the request for a website, for instance, is sent to and answered by a single server identified by its unique IP address. With Unicast, there is no option to address another server (destination).
A Unicast infrastructure is easy to implement and maintain. On the other hand, response times are longer, if the sender and the destination are far apart. And in case of failure of the addressed server, the service is no longer available.
Anycast – Fast and Secure
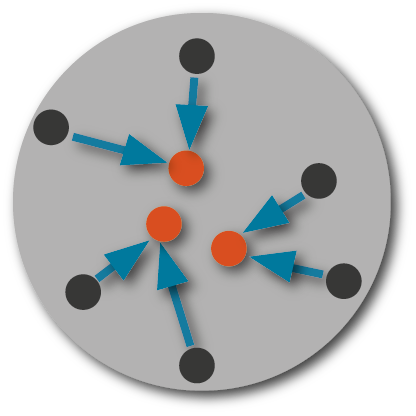
Anycast, in contrast, is a routing and addressing method in which a single unique IP address is served by a whole group of globally dispersed servers. This group is called Anycast cluster or Anycast cloud.
The Anycast routing stands out by ensuring that always the "shortest", that is the most efficient route is chosen in each individual case. This means, a request is answered by the server that can be reached best under the prevailing conditions at that specific point in time, or, in other words, by the nearest server in the network topology.
The Benefits of Anycast Name Service
- Multiple, globally distributed redundant DNS locations with one single IP address guarantee increased availability and reliability and reduced response times.
- If a DNS Anycast server becomes unavailable, the data traffic will be re-routed to an alternate server in the Anycast cluster that is currently the best path.
- Duplicated IP address schemes located in different parts of the worldwide network make DNS service more robust to load peaks and malicious traffic, and thus enhance resilience in case of server outages or attacks.